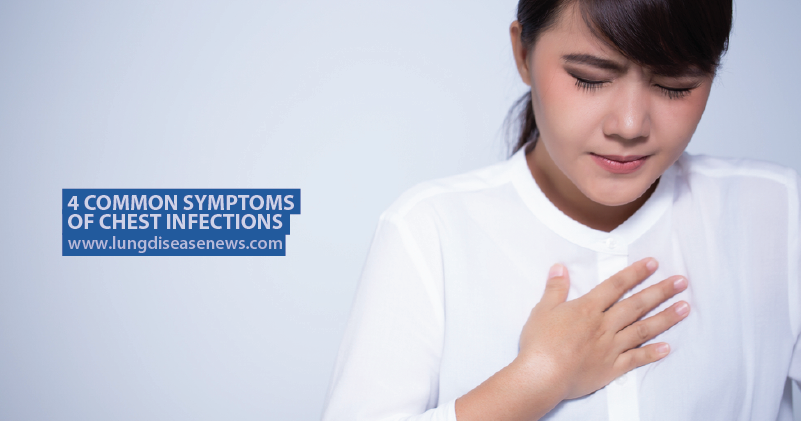
According to the Better Health Channel, a chest infection affects either the larger airways or the smaller air sacs of the lungs. Most chest infections are viruses, meaning that the body’s immune system is enough to fight the infection on its own. However, with most bacterial chest infections, antibiotics are needed.
Chest infections are caused by a virus or bacteria and are particularly rife during winter months. Some chest infections may take a couple days to take hold, whereas some may come on more slowly.
So what are the symptoms of a chest infection?
Symptoms can vary depending on age, the cause of the infection, and any other existing health condition but often include:
Fever. This includes anything from sweating to shivering to chills.
Coughing up phlegm or blood. Phlegm is a thick mucus produced by infection. It could be brown, yellow or green in color.
MORE: 6 Less Common Symptoms of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis